The integration of Embodied AI in autonomous systems is revolutionizing how machines perceive and interact with the physical world. This blog will explore the fundamental concepts of Embodied AI, its applications in robotics and beyond, and the challenges and opportunities it presents for the future of intelligent systems.
Introduction to Embodied AI

Embodied AI refers to the development of intelligent systems that are designed to operate in and learn from the physical world through a physical embodiment, such as a robot or sensor-equipped device. Unlike traditional AI, which primarily operates on abstract data or simulations, Embodied AI connects perception, decision-making, and action with a real-world context. This involves integrating various disciplines like computer vision, natural language processing, robotics, and machine learning to enable systems to interact meaningfully with their environment.
Importance in the Context of Autonomous Systems
The importance of Embodied AI in autonomous systems lies in its ability to bridge the gap between artificial intelligence and real-world functionality. For autonomous systems—whether self-driving cars, robotic assistants, or drones—to operate effectively, they must sense and interpret their surroundings, adapt to dynamic environments, and make decisions in real time. Embodied AI provides the capability to process sensory data, engage with physical spaces, and take purposeful actions, making it an essential component in creating systems that are not only intelligent but also practical and adaptable.
Key Features of Embodied AI
This emerging discipline integrates sophisticated perception, reasoning, and interaction abilities to close the gap between artificial intelligence and the physical world. Some of the key features that characterize embodied AI systems are discussed below.
Perception and Sensing
Perception is the building block of Embodied AI, enabling systems to interpret and make sense of sensory inputs like vision, sound, and touch. This helps autonomous systems recognize objects, understand environments, and learn to function in different conditions. Machine learning algorithms and advanced sensors complement each other to extend this understanding. With precise interpretation of sensory inputs, these systems can seamlessly interact with their environments, enhancing efficiency and reliability for real-world operations.
Navigational and Motor Skills
For Embodied AI to engage with changing environments, solid navigation and motor capabilities are of top priority. Such systems make use of algorithms to compute paths, navigate around obstacles, and carry out intricate movements accurately. Furthermore, they apply methods such as simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) to keep track of their location. With such capabilities integrated, Embodied AI systems can carry out operations such as package delivery, aiding in search and rescue efforts, or even conducting complex surgery.
Learning and Adaptation
A characteristic of Embodied AI is its capacity for learning and adapting over time. Through the application of reinforcement learning and other adaptive algorithms, such systems can sharpen their behavior according to previous experience. This provides ongoing improvement, whether learning a new skill or maximizing performance within dynamic environments. Adaptability means that Embodied AI stays relevant and effective in various applications, from industrial automation to personal service.
Applications of Embodied AI in Autonomous Systems
Below are some of the key applications where Embodied AI is making a significant impact in the development and deployment of autonomous systems:
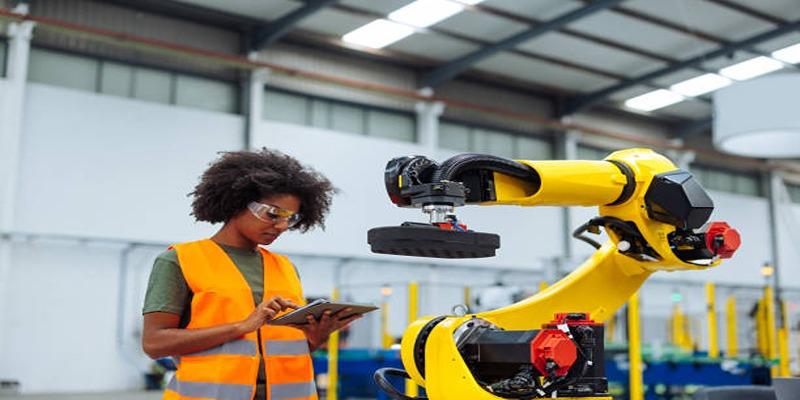
1.Robotics and Industrial Automation
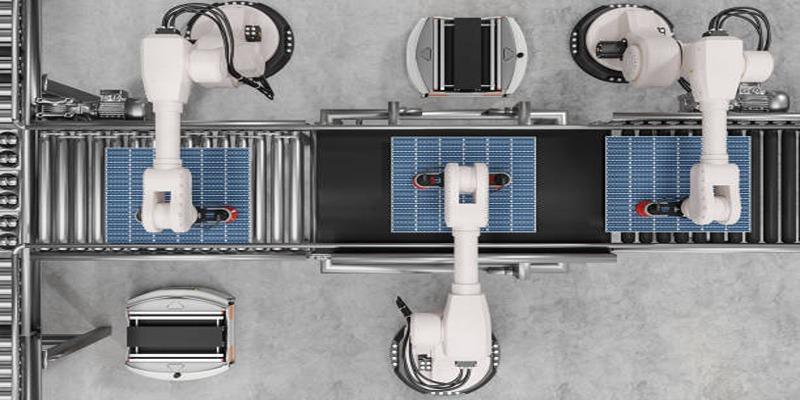
Embodied AI plays a crucial role in robotics and industrial automation, enhancing efficiency and precision in manufacturing processes. By integrating adaptive algorithms, robots can perform complex tasks, learn from their environment, and improve workflows. This reduces human error and supports mass production with consistency.
Furthermore, Embodied AI revolutionizes industries by enabling robots to collaborate with humans safely and intuitively. Its implementation extends to assembly lines, picking and packing operations, and even quality control, providing cost-effective solutions that adapt to evolving production needs.
2.Healthcare and Assistive Technologies
The healthcare industry benefits significantly from Embodied AI, which powers advanced assistive technologies and medical robotics. AI-driven systems can support doctors in surgeries, enable rehabilitation with customized therapies, and enhance patient monitoring through intelligent devices.
They adapt to patients' unique needs, improving overall care quality and accessibility. From robotic exoskeletons aiding mobility to AI companions offering emotional support, Embodied AI improves life for patients and healthcare providers alike. Its versatility ensures that developments in healthcare remain innovative, bridging gaps in treatment and personal well-being.
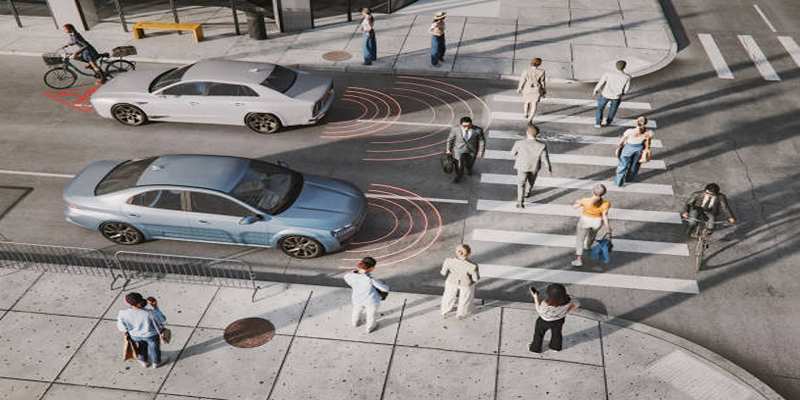
3.Transportation and Self-Driving Vehicles
Transportation systems are evolving with the integration of Embodied AI, particularly in the domain of self-driving vehicles. Autonomous cars and drones leverage sensory inputs and adaptive algorithms to make real-time decisions, ensuring safety and efficiency on the road or in the air.
These systems learn from traffic patterns, weather conditions, and user preferences, constantly refining their navigation abilities. Additionally, Embodied AI supports smart city initiatives, optimizing public transport and reducing congestion. This technology is paving the way for safer, more sustainable, and intelligent transportation networks.
Challenges and Limitations
The development of Embodied AI, while transformative, is not without its challenges. Issues such as data privacy, ethical concerns, and technical limitations present significant hurdles to its widespread implementation.
Data Privacy and Security
As the use of large datasets becomes more prevalent, concerns about how personal information is collected, stored, and used are increasingly significant. Safeguarding sensitive user data from breaches and cyberattacks is critical, alongside ensuring compliance with ever-evolving privacy regulations.
To maintain user trust and protect their rights, organizations must invest in developing robust encryption methods, anonymization techniques, and secure infrastructure. Transparency in data handling practices will also play a vital role in addressing privacy concerns.
Ethical and Societal Concerns
The rise of AI technologies brings forth numerous ethical and societal challenges that need careful consideration. Issues such as biases in AI decision-making, the potential displacement of jobs, and the ethical use of data highlight the need for proactive measures.
Ensuring transparency, fairness, and accountability in AI systems can help mitigate these impacts and build public confidence. Policymakers, researchers, and industries must work together to establish clear guidelines and frameworks that promote inclusivity and minimize harm, ensuring that the benefits of AI are distributed equitably.
Technical and Integration Barriers
Integrating Embodied AI into current systems and infrastructure presents a range of technical hurdles. High implementation costs, compatibility issues with existing technologies, and the demand for reliable and efficient networks are some of the major barriers to adoption.
To unlock the full potential of Embodied AI, consistent advancements in both hardware and software will be required, along with scalable and cost-effective solutions. Collaboration across industries to standardize practices and create adaptable frameworks will be key to overcoming these challenges and enabling seamless integration.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while Embodied AI presents a groundbreaking opportunity to revolutionize various industries, its successful adoption hinges on overcoming significant challenges. By fostering innovation, addressing compatibility concerns, and prioritizing collaboration, we can pave the way for a future where Embodied AI seamlessly integrates into our lives, driving progress and improving the human experience.